Search the Special Collections and Archives Portal
Search Results

Correspondence, Levi Syphus to Sadie George
Date
1907-05-31
Archival Collection
Description
This folder is from the "Correspondence" file of the Sadie and Hampton George Papers (MS-00434)
Text

Postcard of Klondyke (Nev.), 1963
Date
1963
Archival Collection
Description
Located 10 miles southeast of Tonopah, the camp was settled in the late 1890s when silver and gold was discovered in the area. In May, 1900, when Jim Butler picked up his first samples at the site that would become Tonopah, he was en route to Klondyke. He offered the local assayer, Frank Higgs, an interest in the find for an assay, but Higgs declared the samples worthless and threw them out. Fortunately, Butler retrieved more samples on this return trip to Belmont. The building on the right with the large smoke-stack was the assay office. None of the structures remain today.
Image

Placer mining claim, notarized
Date
1901-01-31
Archival Collection
Description
This folder is from "Legal Records" file of the Sadie and Hampton George Papers (MS-00434)
Text

Mining claim: H. George and Elinor Syphyus
Date
1901-01-31
Archival Collection
Description
This folder is from "Legal Records" file of the Sadie and Hampton George Papers (MS-00434)
Text

Goldfield Review: newspaper issue
Date
1907-08-17
Archival Collection
Description
From the C. A. Earle Rinker Papers (MS-00514) -- Series III: Maps, newspapers, souvenirs, and ephemera -- Newspapers from Goldfield, Nevada and various locations.
Text
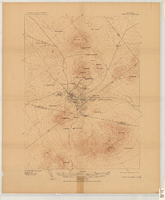
Tonopah, Nevada mining map, March 1904
Date
1904-03
Description
'U.S. Geological Survey, George Otis Smith, Director.' 'R.U. Goode, Geographer in charge. Triangulation by U.S. Coast and Geodetic Survey. Topography by W.J. Peters. Surveyed in 1902-1903.' 'Edition of Mar. 1904, reprinted Apr. 1910.' Oriented with north toward the upper left. Relief shown by contours and hachures. Scale 1:12,000 (W 117°14´--W 117°12´/N 38°05´--N 38°03´)
Text

Postcard of the Harmill silver-lead mine, Montezuma (Nev.), 1929
Date
1929
Archival Collection
Description
The Harmill was being operated by Gerald B. Hartley, Sr. and was worked through the 1930s. (Gerald B. Hartley, Jr. Collection) There was an inscription on the image. "The Montezuma district was laid out after the discovery of ore in the area on May 24, 1867 by Thomas Nagle, Mat Plunkett, and a Mr. Carlyle. The district was active through the 1880s after which mining came to a standstill. Montezuma experienced a revival in the early 1900s on the heels of the Goldfield boom. Mining continued through the 1930s from operations such as the Harmill. Ore was chiefly silver accompanied by lead with some gold. Recorded production from the district was over $500,000."
Image

San Francisco Call - Nevada Edition: newspaper issue
Date
1905-05-23
Archival Collection
Description
From the C. A. Earle Rinker Papers (MS-00514) -- Series III: Maps, newspapers, souvenirs, and ephemera -- Newspapers from Goldfield, Nevada and various locations.
Text

Correspondence, W.H. Clarke to Levi Syphus
Date
1905-02-09
Archival Collection
Description
This folder is from the "Correspondence" file of the Sadie and Hampton George Papers (MS-00434)
Text

Authorization to sell mining interests
Date
1909-11-05
Archival Collection
Description
This folder is from "Legal Records" file of the Sadie and Hampton George Papers (MS-00434)
Text
Pagination
Refine my results
Content Type
Creator or Contributor
Subject
Archival Collection
Digital Project
Resource Type
Material Type
Place
Language
Records Classification
