Search the Special Collections and Archives Portal
Search Results
Audio clip from interview with George Simmons conducted by Claytee D. White, December 13, 2013
Date
2013-12-13
Archival Collection
Description
Audio clip from interview with George Simmons. In this clip, Simmons talks about his work with Sproul Homes in Las Vegas and his career designing homes and structures for Test Site.
Sound

Photographs of Pabst Blue Ribbon sign, Las Vegas (Nev.), June 28, 2017
Date
2017-06-28
2017-07-22
Archival Collection
Description
The Pabst Blue Ribbon sign sits near the intersection of Fremont Street and North Las Vegas Boulevard in Downtown Las Vegas. Information about the sign is available in the Southern Nevada Neon Survey Sheet.
Site address: Fremont St and Las Vegas Blvd
Sign owner: PBR Donated, but a part of Fremont Street East
Sign details: PBR held a revealing party when installed in 2015, right next to The Park on Fremont. YESCO manufactured the 30 feet tall sign is nicknamed Cool Blue. Previous to this sign in this location the Maharaja Hookah Cafe had their signage in the same location previous to 2013.
Sign condition: 5, just installed in 2015 so neon and paint are still in great condition
Sign form: Free Standing Sign
Sign-specific description: 30 feet tall, the sign is nicknamed Cool Blue. A 30 foot waiter holding his arm out with 3 beers on his arm and one in his hand. The beers are animated with them lighting up in order starting with the one closest to his body. His arm is resting on a PBR can. The waiters shirt and cheeks illuminate red neon while the rest of his body illuminates blue argon. The PBR beer can illuminates red and blue as well.
Sign - type of display: Neon
Sign - media: Steel
Sign animation: The Beer cans on the waiters arm light up in order, starting with the one closest to his body.
Sign environment: This is located in the parking lot on the corner of Las Vegas Blvd. North and Fremont St. East next to the Park on Fremont. This marks the beginning of the Fremont Street East District were other freestanding Neon signs are as well.
Sign manufacturer: YESCO
Sign - date of installation: 2015
Sign - thematic influences: The retro theme makes it look like a throwback to 1950s/60s advertisement. Also since it is for a beer company it shows that Neon does not always have to be for the Casinos here in Vegas. This is one of the first freestanding signs you see in the Fremont Street East District, thus showing that the Neon community downtown still is thriving and still defines our culture here.
Survey - research locations: YESCO website http://www.yesco.com/news/yesco-installs-pabst-blue-ribbon-neon-sign/ , Vital Vegas website https://vitalvegas.com/downtowns-fremont-east-gets-a-new-neon-sign-courtesy-of-pbr/ , google map roadside view
Survey - research notes: Since this is a freestanding sign it is difficult to find any specific information on a single owner or why this sign was placed there specifically.
Surveyor: Emily Fellmer
Survey - date completed: 2017-07-22
Sign keywords: Neon; Steel; Back to back; Monument sign
Site address: Fremont St and Las Vegas Blvd
Sign owner: PBR Donated, but a part of Fremont Street East
Sign details: PBR held a revealing party when installed in 2015, right next to The Park on Fremont. YESCO manufactured the 30 feet tall sign is nicknamed Cool Blue. Previous to this sign in this location the Maharaja Hookah Cafe had their signage in the same location previous to 2013.
Sign condition: 5, just installed in 2015 so neon and paint are still in great condition
Sign form: Free Standing Sign
Sign-specific description: 30 feet tall, the sign is nicknamed Cool Blue. A 30 foot waiter holding his arm out with 3 beers on his arm and one in his hand. The beers are animated with them lighting up in order starting with the one closest to his body. His arm is resting on a PBR can. The waiters shirt and cheeks illuminate red neon while the rest of his body illuminates blue argon. The PBR beer can illuminates red and blue as well.
Sign - type of display: Neon
Sign - media: Steel
Sign animation: The Beer cans on the waiters arm light up in order, starting with the one closest to his body.
Sign environment: This is located in the parking lot on the corner of Las Vegas Blvd. North and Fremont St. East next to the Park on Fremont. This marks the beginning of the Fremont Street East District were other freestanding Neon signs are as well.
Sign manufacturer: YESCO
Sign - date of installation: 2015
Sign - thematic influences: The retro theme makes it look like a throwback to 1950s/60s advertisement. Also since it is for a beer company it shows that Neon does not always have to be for the Casinos here in Vegas. This is one of the first freestanding signs you see in the Fremont Street East District, thus showing that the Neon community downtown still is thriving and still defines our culture here.
Survey - research locations: YESCO website http://www.yesco.com/news/yesco-installs-pabst-blue-ribbon-neon-sign/ , Vital Vegas website https://vitalvegas.com/downtowns-fremont-east-gets-a-new-neon-sign-courtesy-of-pbr/ , google map roadside view
Survey - research notes: Since this is a freestanding sign it is difficult to find any specific information on a single owner or why this sign was placed there specifically.
Surveyor: Emily Fellmer
Survey - date completed: 2017-07-22
Sign keywords: Neon; Steel; Back to back; Monument sign
Mixed Content

Photographs of Vanguard Lounge sign, Las Vegas (Nev.), June 28, 2017
Date
2017-06-28
2017-08-11
Archival Collection
Description
The Vanguard Lounge sits at 516 Fremont Street in Downtown Las Vegas. Information about the sign is available in the Southern Nevada Neon Survey Sheet.
Site address: 516 Fremont St
Sign owner: Andrew and Jennifer Wheatley
Sign details: The building was originally constructed in 1951. Previously to the lounge opening it was Fremont Street Guitars. Andrew and Jennifer Wheatley opened the lounge in 2010 after 30 years of experience together in the industry. This trendy bar has Modern-Industrial Decor, as you can see with their black building with a glass garage door entrance.
Sign condition: 5- newer sign that lights up brightly at night
Sign form: Hanging sign
Sign-specific description: Right above the entrance is a black canopy, but at night a white neon tube illuminates the perimeter of the canopy. The canopy also showcases their street address 516 in white channeled numbers. Above the canopy there is a beam which acts as a support for their main sign. Their main sign is a black rectangle which is also attached to the building. The sign states Vanguard Lounge in white skeletal neon letters. The word Vanguard is in a thick block-type print letters. Lounge is written in a smaller but similar type-font.
Sign - type of display: Neon
Sign - media: Steel
Sign environment: This is located in the Fremont East district in between Las Vegas Blvd. and 6th St. This locations storefront is located in between the Therapy restaurant and Red dance club (used to be the old Coin Insert bar).
Sign manufacturer: Valley Signs and Lighting
Sign - date of installation: 2010
Sign - date of redesign/move: Vanguard used the old sign box that the previous company used and added their logo in neon in 2010.
Sign - thematic influences: The skeletal neon showcases a simple yet classic design. It also showcases the Modern trendy vibe.
Sign - artistic significance: The sign does have a modern vibe but is staying true to the Neon culture of downtown.
Survey - research locations: Vanguard lounge website http://www.vanguardlv.com/vanguard_lounge_venue , Las Vegas Sun https://lasvegassun.com/news/2010/sep/20/vanguard-lounge-opens-fremont-street/ , Assessor's page
Survey - research notes: Definition of Vanguard is a group of people leading the way in new developments/ideas. This is possibly alluding to their theme of being different than the other bars downtown. Coincidentally there was a dance club in L.A. also called Vanguard, but no connection found between the properties besides their modern dance vibes.
Surveyor: Emily Fellmer
Survey - date completed: 2017-08-11
Sign keywords: Neon; Steel; Hanging; Pole sign; Roof Sign
Site address: 516 Fremont St
Sign owner: Andrew and Jennifer Wheatley
Sign details: The building was originally constructed in 1951. Previously to the lounge opening it was Fremont Street Guitars. Andrew and Jennifer Wheatley opened the lounge in 2010 after 30 years of experience together in the industry. This trendy bar has Modern-Industrial Decor, as you can see with their black building with a glass garage door entrance.
Sign condition: 5- newer sign that lights up brightly at night
Sign form: Hanging sign
Sign-specific description: Right above the entrance is a black canopy, but at night a white neon tube illuminates the perimeter of the canopy. The canopy also showcases their street address 516 in white channeled numbers. Above the canopy there is a beam which acts as a support for their main sign. Their main sign is a black rectangle which is also attached to the building. The sign states Vanguard Lounge in white skeletal neon letters. The word Vanguard is in a thick block-type print letters. Lounge is written in a smaller but similar type-font.
Sign - type of display: Neon
Sign - media: Steel
Sign environment: This is located in the Fremont East district in between Las Vegas Blvd. and 6th St. This locations storefront is located in between the Therapy restaurant and Red dance club (used to be the old Coin Insert bar).
Sign manufacturer: Valley Signs and Lighting
Sign - date of installation: 2010
Sign - date of redesign/move: Vanguard used the old sign box that the previous company used and added their logo in neon in 2010.
Sign - thematic influences: The skeletal neon showcases a simple yet classic design. It also showcases the Modern trendy vibe.
Sign - artistic significance: The sign does have a modern vibe but is staying true to the Neon culture of downtown.
Survey - research locations: Vanguard lounge website http://www.vanguardlv.com/vanguard_lounge_venue , Las Vegas Sun https://lasvegassun.com/news/2010/sep/20/vanguard-lounge-opens-fremont-street/ , Assessor's page
Survey - research notes: Definition of Vanguard is a group of people leading the way in new developments/ideas. This is possibly alluding to their theme of being different than the other bars downtown. Coincidentally there was a dance club in L.A. also called Vanguard, but no connection found between the properties besides their modern dance vibes.
Surveyor: Emily Fellmer
Survey - date completed: 2017-08-11
Sign keywords: Neon; Steel; Hanging; Pole sign; Roof Sign
Mixed Content

Photograph of the "Mole" Jarva Tunnel Borer breaking through the tunnel on the Las Vegas River Mountain Project, Las Vegas, Nevada, circa 1968-1971
Date
1968 to 1971
Archival Collection
Description
Another shot of the "mole" Jarva Tunnel Borer poking its nose out of the tunnel through mountain as work on the Las Vegas River Mountains Project progresses. The first stage of construction was completed between 1968-1971, and is comprised of a main aqueduct, a 3.78 mile tunnel through the River Mountains, eight pumping plants, and 31.4 miles of pipeline. This stage has a peaking capacity of 26.7 million cubic feet of potable water per day. The second stage enlarged the first stage system by expanding some of the existing facilities. New features included five pumping plants, the second barrel to the main aqueduct, and about 30 miles of pipeline and laterals with surge tanks, regulating tanks, and other delivery facilities. In conjunction with this stage, the State of Nevada enlarged and modified the Alfred Merritt Smith water treatment facilities to accommodate additional water supplies. The River Mountains Tunnel was constructed to full capacity in the first stage, and the Saddle Island intake facilities were oversized to accommodate both stages. The aqueduct system has a peaking capability of 53.4 million cubic feet of water per day. The River Mountains Tunnel was constructed during the first stage to accommodate second stage expansion. It is 3.78 miles long and was excavated through the River Mountains, which lie between Las Vegas Valley and Lake Mead. The concrete-lined tunnel has an inside diameter of 121.5 inches, and a maximum capacity of 608 cfs. The SNWA also constructed a larger tunnel, parallel to the River Mountains Tunnel for further expansion. The River Mountains Tunnel is used to convey raw water from Lake Mead to the River Mountains Water Treatment Facility that SNWA constructed near Henderson, NV. The River Mountains Facility, which began delivering treated water in October 2002, treats up to 300 million gallons of water per day, and was designed so it can expand to meet Southern Nevada's needs. In the future, the River Mountains facility will be able to treat up to 600 million gallons of water a day. This facility provides additional reliability and capacity to Southern Nevada's municipal water treatment and distribution capabilities.
Image

Photograph of the 988 caterpillar loader towing mole and conveyor to the tunnel portal used on the Las Vegas River Mountain Project, Las Vegas, Nevada, circa 1968-1971
Date
1968 to 1971
Archival Collection
Description
A front view taken from above of the outlet portal showing the 988 caterpillar loader towing mole and conveyor to the tunnel portal. The first stage of construction was completed between 1968-1971, and is comprised of a main aqueduct, a 3.78 mile tunnel through the River Mountains, eight pumping plants, and 31.4 miles of pipeline. This stage has a peaking capacity of 26.7 million cubic feet of potable water per day. The second stage enlarged the first stage system by expanding some of the existing facilities. New features included five pumping plants, the second barrel to the main aqueduct, and about 30 miles of pipeline and laterals with surge tanks, regulating tanks, and other delivery facilities. In conjunction with this stage, the State of Nevada enlarged and modified the Alfred Merritt Smith water treatment facilities to accommodate additional water supplies. The River Mountains Tunnel was constructed to full capacity in the first stage, and the Saddle Island intake facilities were oversized to accommodate both stages. The aqueduct system has a peaking capability of 53.4 million cubic feet of water per day. The River Mountains Tunnel was constructed during the first stage to accommodate second stage expansion. It is 3.78 miles long and was excavated through the River Mountains, which lie between Las Vegas Valley and Lake Mead. The concrete-lined tunnel has an inside diameter of 121.5 inches, and a maximum capacity of 608 cfs. The SNWA also constructed a larger tunnel, parallel to the River Mountains Tunnel for further expansion. The River Mountains Tunnel is used to convey raw water from Lake Mead to the River Mountains Water Treatment Facility that SNWA constructed near Henderson, NV. The River Mountains Facility, which began delivering treated water in October 2002, treats up to 300 million gallons of water per day, and was designed so it can expand to meet Southern Nevada's needs. In the future, the River Mountains facility will be able to treat up to 600 million gallons of water a day. This facility provides additional reliability and capacity to Southern Nevada's municipal water treatment and distribution capabilities.
Image
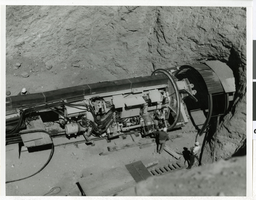
Photograph of the outlet portal showing the mole preparing to walk into the tunnel on the Las Vegas River Mountain Project, Las Vegas, Nevada, circa 1968-1971
Date
1968 to 1971
Archival Collection
Description
A close-up view looking down from the left side of the outlet portal showing the mole preparing to walk into the tunnel. Three unidentified men can be seen working near the mole. The first stage of construction was completed between 1968-1971, and is comprised of a main aqueduct, a 3.78 mile tunnel through the River Mountains, eight pumping plants, and 31.4 miles of pipeline. This stage has a peaking capacity of 26.7 million cubic feet of potable water per day. The second stage enlarged the first stage system by expanding some of the existing facilities. New features included five pumping plants, the second barrel to the main aqueduct, and about 30 miles of pipeline and laterals with surge tanks, regulating tanks, and other delivery facilities. In conjunction with this stage, the State of Nevada enlarged and modified the Alfred Merritt Smith water treatment facilities to accommodate additional water supplies. The River Mountains Tunnel was constructed to full capacity in the first stage, and the Saddle Island intake facilities were oversized to accommodate both stages. The aqueduct system has a peaking capability of 53.4 million cubic feet of water per day. The River Mountains Tunnel was constructed during the first stage to accommodate second stage expansion. It is 3.78 miles long and was excavated through the River Mountains, which lie between Las Vegas Valley and Lake Mead. The concrete-lined tunnel has an inside diameter of 121.5 inches, and a maximum capacity of 608 cfs. The SNWA also constructed a larger tunnel, parallel to the River Mountains Tunnel for further expansion. The River Mountains Tunnel is used to convey raw water from Lake Mead to the River Mountains Water Treatment Facility that SNWA constructed near Henderson, NV. The River Mountains Facility, which began delivering treated water in October 2002, treats up to 300 million gallons of water per day, and was designed so it can expand to meet Southern Nevada's needs. In the future, the River Mountains facility will be able to treat up to 600 million gallons of water a day. This facility provides additional reliability and capacity to Southern Nevada's municipal water treatment and distribution capabilities.
Image

Photograph of Key federal, state and contractor representatives who were on hand when the mole broke through the tunnel, Las Vegas, Nevada, 6-26-69
Date
1969-06-26
Archival Collection
Description
A group of 13 key federal, state and contractor representatives who were on hand when the mole broke through the tunnel on 6-26-69. Two unidentified workers are visible above them with the "mole." The first stage of construction was completed between 1968-1971, and is comprised of a main aqueduct, a 3.78 mile tunnel through the River Mountains, eight pumping plants, and 31.4 miles of pipeline. This stage has a peaking capacity of 26.7 million cubic feet of potable water per day. The second stage enlarged the first stage system by expanding some of the existing facilities. New features included five pumping plants, the second barrel to the main aqueduct, and about 30 miles of pipeline and laterals with surge tanks, regulating tanks, and other delivery facilities. In conjunction with this stage, the State of Nevada enlarged and modified the Alfred Merritt Smith water treatment facilities to accommodate additional water supplies. The River Mountains Tunnel was constructed to full capacity in the first stage, and the Saddle Island intake facilities were oversized to accommodate both stages. The aqueduct system has a peaking capability of 53.4 million cubic feet of water per day. The River Mountains Tunnel was constructed during the first stage to accommodate second stage expansion. It is 3.78 miles long and was excavated through the River Mountains, which lie between Las Vegas Valley and Lake Mead. The concrete-lined tunnel has an inside diameter of 121.5 inches, and a maximum capacity of 608 cfs. The SNWA also constructed a larger tunnel, parallel to the River Mountains Tunnel for further expansion. The River Mountains Tunnel is used to convey raw water from Lake Mead to the River Mountains Water Treatment Facility that SNWA constructed near Henderson, NV. The River Mountains Facility, which began delivering treated water in October 2002, treats up to 300 million gallons of water per day, and was designed so it can expand to meet Southern Nevada's needs. In the future, the River Mountains facility will be able to treat up to 600 million gallons of water a day. This facility provides additional reliability and capacity to Southern Nevada's municipal water treatment and distribution capabilities.
Image

Photograph of Key federal, state and contractor representatives who were on hand when the mole broke through the tunnel, Las Vegas, Nevada, 6-26-69
Date
1969-06-26
Archival Collection
Description
A group of 16 key federal, state and contractor representatives who were on hand when the mole broke through the tunnel on 6-26-69. Two unidentified workers are visible above them with the "mole." The first stage of construction was completed between 1968-1971, and is comprised of a main aqueduct, a 3.78 mile tunnel through the River Mountains, eight pumping plants, and 31.4 miles of pipeline. This stage has a peaking capacity of 26.7 million cubic feet of potable water per day. The second stage enlarged the first stage system by expanding some of the existing facilities. New features included five pumping plants, the second barrel to the main aqueduct, and about 30 miles of pipeline and laterals with surge tanks, regulating tanks, and other delivery facilities. In conjunction with this stage, the State of Nevada enlarged and modified the Alfred Merritt Smith water treatment facilities to accommodate additional water supplies. The River Mountains Tunnel was constructed to full capacity in the first stage, and the Saddle Island intake facilities were oversized to accommodate both stages. The aqueduct system has a peaking capability of 53.4 million cubic feet of water per day. The River Mountains Tunnel was constructed during the first stage to accommodate second stage expansion. It is 3.78 miles long and was excavated through the River Mountains, which lie between Las Vegas Valley and Lake Mead. The concrete-lined tunnel has an inside diameter of 121.5 inches, and a maximum capacity of 608 cfs. The SNWA also constructed a larger tunnel, parallel to the River Mountains Tunnel for further expansion. The River Mountains Tunnel is used to convey raw water from Lake Mead to the River Mountains Water Treatment Facility that SNWA constructed near Henderson, NV. The River Mountains Facility, which began delivering treated water in October 2002, treats up to 300 million gallons of water per day, and was designed so it can expand to meet Southern Nevada's needs. In the future, the River Mountains facility will be able to treat up to 600 million gallons of water a day. This facility provides additional reliability and capacity to Southern Nevada's municipal water treatment and distribution capabilities.
Image
Pagination
Refine my results
Content Type
Creator or Contributor
Subject
Archival Collection
Digital Project
Resource Type
Year
Material Type
Place
Language
Records Classification


