Search the Special Collections and Archives Portal
Search Results
Southern Nevada Memorial Hospital Records
Identifier
Abstract
The Southern Nevada Memorial Hospital Records (1955-1956) consist of Southern Nevada Memorial Hospital (SNMH) records including minutes of Board of Trustees meetings, Grand Jury accusations against the Board regarding the poor operation of the hospital, the Board's responses, and newspaper clippings from the Las Vegas Review-Journal regarding this controversy.
Archival Collection

Book B of the Mining Records of El Dorado Mining District, Lincoln Co., Nevada, opened January 1888
Date
Description
Text

Unidentified crowd of people Nevada Test Site, Nevada: photographic slide
Date
Archival Collection
Description
From the Sister Klaryta Antoszewska Photograph Collection (PH-00352). Appear to be waiting for a test bombing.
Image

A slide of the neon sign for the Nevada Club, Laughlin, Nevada 1986
Date
Archival Collection
Description
Image

Children of Giovanni Fallini at the Eden Creek Ranch, Nevada: photographic print
Date
Archival Collection
Description
From the Nye County, Nevada Photograph Collection (PH-00221) -- Series VII. Other areas in Nye County -- Subseries VII.C. Fallini Family (Twin Springs, Nevada). Included are Joe, Raymond, Mildred, and Ethel Fallini. Joe Fallini is the smallest child.
Image

Miners pictured at a mine site perhaps in the vicinity of Round Mountain, Nevada: photographic print
Date
Archival Collection
Description
From the Nye County, Nevada Photograph Collection (PH-00221) -- Series V. Smoky Valley, Nevada and Round Mountain, Nevada -- Subseries V.C. Lofthouse-Berg Families (Round Mountain)
Image
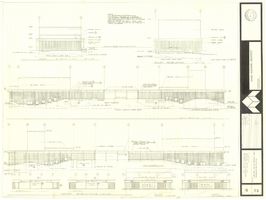
Architectural drawing of concert hall and drama theater, University of Nevada, Las Vegas, exterior elevations, November 5, 1969
Date
Archival Collection
Description
Exterior elevations for the concert hall and drama theater on the University of Nevada, Las Vegas campus, including a connecting courtyard. These buildings would become the Artemus W. Ham Concert Hall and the Judy Bayley Theatre. Sheet 6 of 35. "Drawn by G.T. Checked by K.D. Job number 6828. Scale 1/16" = 1'-0". Date Nov. 5, 1969"
Site Name: University of Nevada, Las Vegas
Address: 4505 S. Maryland Parkway
Image

Letter from John M. Bunker, St Thomas, Nevada to Etta M Syphus, Panaca, Nevada
Date
Archival Collection
Description
From the Syphus-Bunker Papers (MS-00169). The folder contains an original handwritten letter and a typed transcription of the same letter.
Text

Film transparency of a ghost town, Delamar, Nevada, 1956
Date
Archival Collection
Description
Image

Film transparency of a ghost town, Delamar, Nevada, 1956
Date
Archival Collection
Description
Image
