Search the Special Collections and Archives Portal
Search Results
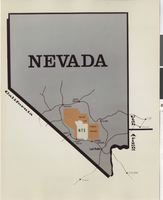
Map of Nevada Test Site: photographic print
Date
1945-19-82
Archival Collection
Description
Map of Nevada showing Nevada Test Site.
Image
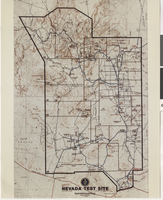
Updated map of the Nevada Test Site: photographic print
Date
1982
Archival Collection
Description
Updated 1982 map of Nevada Test Site.
Image

Main Base Camp at Nevada Test Site, Mercury: photographic print
Date
1945-19-82
Archival Collection
Description
Mercury, the Main Base Camp at Nevada Test Site (NTS). The camp provides overnight accommodations for more than 950 people. It is a warehousing, communication, repair, fabrication and field administration center.
Image

Radioactive waste management site at Frenchman Flat: photographic print
Date
1945-19-82
Archival Collection
Description
The radioactive waste management site at Frenchman Flat (area 5) provides surface storage and trench disposal of contaminated materials with low levels of radioactivity at the Nevada Test Site (NTS).
Image

Gate 100 into the Nevada Test Site: photographic print
Date
1945-19-82
Archival Collection
Description
Security guards check access badges at Gate 100, Nevada Test Site (NTS). The NTS is closed to the public, except for people on official business. The Test Site was dedicated as a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Environmental Research Park in 1992.
Image

Landscape view of the IDECO 2500: photographic print
Date
1945-19-82
Archival Collection
Description
The IDECO 2500, used at the Nevada Test Site, is a 2000 horsepower diesel electric rig capable of drilling holes 72 to 140 inches in diameter to depths of 4000 feet.
Image

Inside view of Control Point at the Nevada Test Site: photographic print
Date
1945-19-82
Archival Collection
Description
Inside the Control Point at the Nevada Test Site the Test Controller (at table) prepares to conduct a nuclear test. Members of the Test Controller's Advisory Panel (at table) are experts in nuclear weapons, meteorology, radiation, and nuclear medicine.
Image

Signal cables laid out at Yucca Flats: photographic print
Date
1945-19-82
Archival Collection
Description
Signal cables laid out at a test location on Yucca Flats, the principal underground nuclear weapons testing area at Nevada Test Site (NTS).
Image

Craters at the Nevada Test Site: photographic print
Date
1945-19-82
Archival Collection
Description
Final test preparations (at the Nevada Test Site) include running miles of cable down hole. A rack containing instrumentation to go down hole is assembled in the tower to the right. Subsidence craters from earlier underground tests dot landscape.
Image

Fabrication of line-of-sight pipes: photographic print
Date
1945-19-82
Archival Collection
Description
Line-of-sight pipes are fabricated inside tunnels at Rainier Mesa on Department of Energy's Nevada Test Site. The Department of Energy works with the Defense Nuclear Agency in measuring the effects of blast-produced radiation on military hardware.
Image
Pagination
Refine my results
Content Type
Creator or Contributor
Subject
Archival Collection
Digital Project
Resource Type
Year
Material Type
Place
Language
